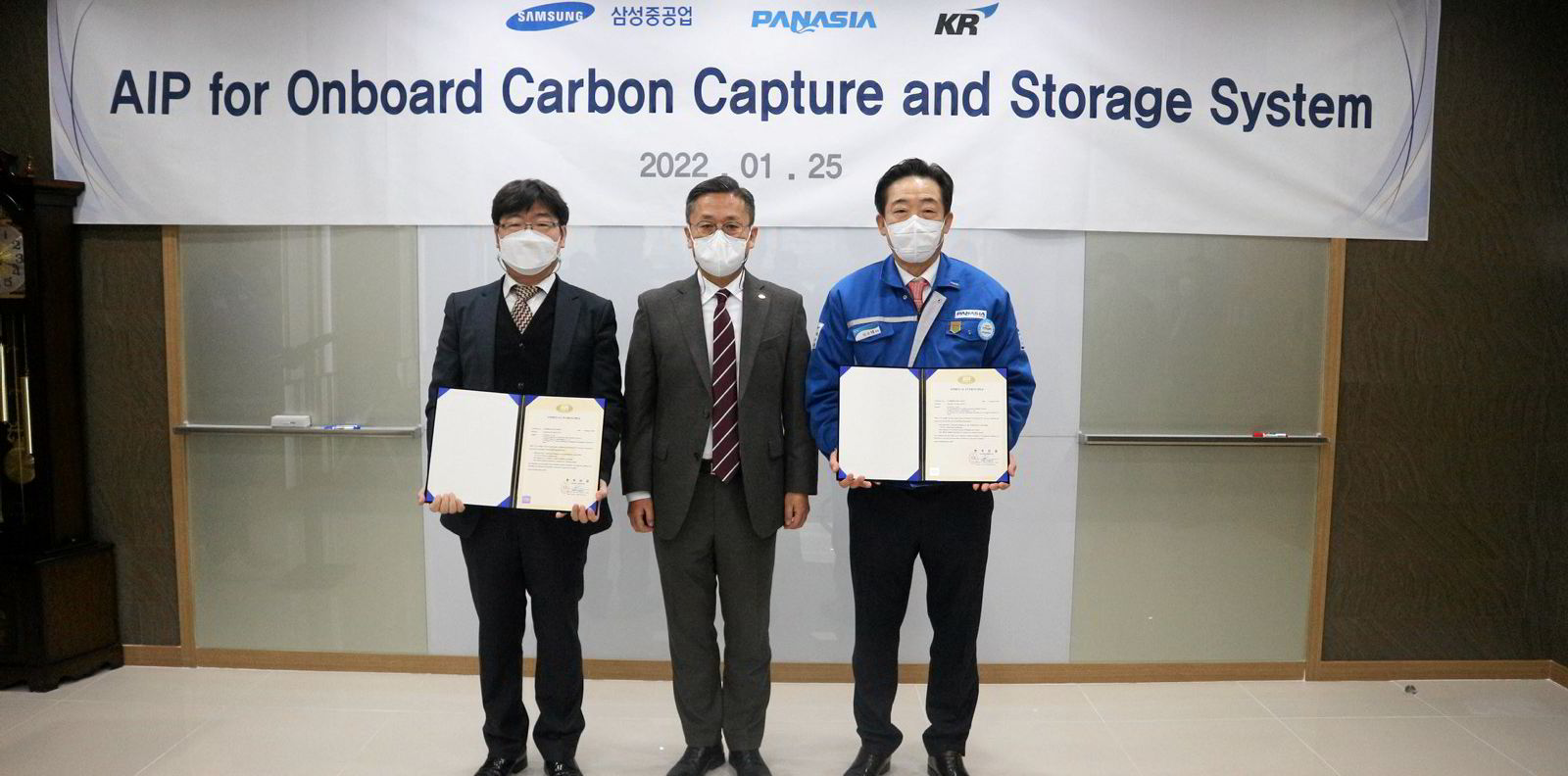
Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) has developed an onboard carbon capture system for conventionally-fuelled vessels that is also applicable to LNG-powered ships.
The South Korean shipyard said it has developed the system together with Panasia, one of South Korea’s leading marine equipment manufacturers and an energy system expert.
SHI said system has been granted approval-in-principle from the Korean Register of Shipping.
It plans to make it available in the market by 2024.
The yard said the green technology system uses amine-based liquid absorbent to separate and collect CO2 from the exhaust gas of fuel that is burnt in a ship's engine or generator.
“Samsung and Panasia have jointly developed the technology since 2020, recognising the necessity for carbon reduction technology to achieve carbon neutrality,” the shipbuilder said in a statement.
SHI is conducting performance testing of the system at Panasia's demonstration facility in Jinhae.
“A combination of LNG powered propulsion and carbon capture technology is expected to be an economically viable solution against forthcoming IMO’s carbon emissions regulations, which will be strengthened in stages by 2050,” said Geon-il Park, director of Green Energy Technology Center at SHI.
“The technology will not only help achieve greenhouse gas reduction goals in the maritime sector, but also boost demand for LNG-fuelled vessels.”
SHI has calculated that globally, there are 251 LNG-fuelled ships trading, and a further 403 on order or under construction.
Last year, the shipbuilder signed an agreement with German technology company BASF’s OASE Gas Treatment team to expand its technological cooperation based on OASE's blue CO2 capture process technology, which allows the capturing of CO2 from exhaust gas on board vessels.